You are starting your new business and working whole day long even till midnight because you love it. You believe you are doing something great and you are trying to do it in a best way. You are thinking about hundreds of issues regarding your financial strtategy, marketing strategy and organizational strategy .However, what’s about your production plan of your business?
I mean, what are you going to do to produce your product in a cost-efficient manner? Say, you have almost 30 suppliers for your input materials. Are you getting your all input materials you need to process and assemble in a definite span of time to make the product ready for the customers? Are you counting extra time and cost for warehousing the unfinished products because of delayed arrival of some input materials from your suppliers? If yes, then you are not doing it in a best way that you want. You know, you can gain an advantage over your competitors by minimizing your cost. You can brand your company as cost-efficient like Toyota, Wal-Mart by reducing the internal cost.
To minimize your cost, you don’t need to compromise with your product quality; you just need to eliminate your waste. Yes, I am talking about 7 wastes. Shigeo Shingo, one of the worlds’s leading experts on manufacturing practices and the Toyota Production System identified “Seven” forms of wastes. By eliminating these wastes you can improve your cost efficiency and responsivess to the customers. Let’s have a focus on those wastes.
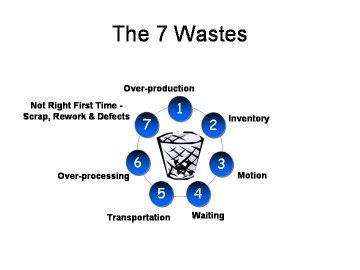
Waste no 1: Overproduction
To manage your production process you may have a Material Resource Planning (MRP, used to refer production planning and inventory control system).But If you don’t have a customer focus you can produce more than customers’ demand by using your resources. To avoid this waste you can follow Kanban(Japanese term that refers a scheduling system that tells you what to produce, when to produce it, and how much to produce.)I mean first follow Kanban and on the basis of it make MRP to discharge overproduction.
Waste no 2: Inventory
If you work with a lengthy production process you have to deal with raw materials, work in Progress (WIP) or finished goods in the same time. But how much of each of them is needed in real time to make the ultimate product is a big question. Some of them may not add any value to the ultimate products. It can be caused by inaccurate forecasting, lack of leveling production schedule and unreliable suppliers.
Waste no 3: Excess Motion
Here, motion means movement of workers. Motion turns into waste when a worker moves more than necessary for the process to be completed. It causes waste of time and efficiency. For example, a worker works with two machines placed distantly which could be placed more closely. He has to move between these distant places frequently that reduces his efficiency and productivity. It is mainly caused by lack of standard operation procedure, poorly designed workspace and inadequate training.
Waste no 4: Waiting

Sometimes you will see that your workers or some of the parts have to wait for a work cycle to be completed. Say, you have 10 parts to assemble and assembling task is completed using 4 stages. For each stage you have employed 4 workers. If your channel members supply parts lately, if you lack multi-skilling and flexibility in production system then the workers of any of the steps may have to wait for the work cycle to be completed. It will always increase your cost and time needed.
Waste no 5: Transportation
If you look carefully to the movement of parts you will see sometimes the parts are moving unnecessarily. For example, some of the raw materials may be transported to a stage where it is not necessary or the raw materials are stored in a place from where it is difficult to move them to the assembling or processing space. It increases production time and consumes resource & floor space. Badly designed process, complex material flows and sharing of equipment can causes such unnecessary movements.
Waste no 6: Over-Processing
You have to process your product to the level that customers demand. You may have technology and other resources to process the product further. But you shouldn’t do it because you know ultimately you have to fulfill the customers demand, not more than that. Processing beyond the standard will consume your resources and production time. It can be caused by the out-of-date standards, lack of innovation and improvement etc.
Waste no 7: Defects
Frequent findings of defects can reduce your customers’ satisfaction. You know, customer can treat your product as a defective not only for the scrap or bent product but also for the quality below the standard. Incapable processes, lack of skill, training, inaccurate design and engineering, machine inaccuracy can cause product defects.
A large portion of middle class people always prefer cost-efficient brands. By minimizing these 7 wastes you can introduce your product as cost-efficient brand. As a Start-up Enterprise if your firm can establish a cost-efficient brand in the early age you can do far better business than your competitors in the market.
